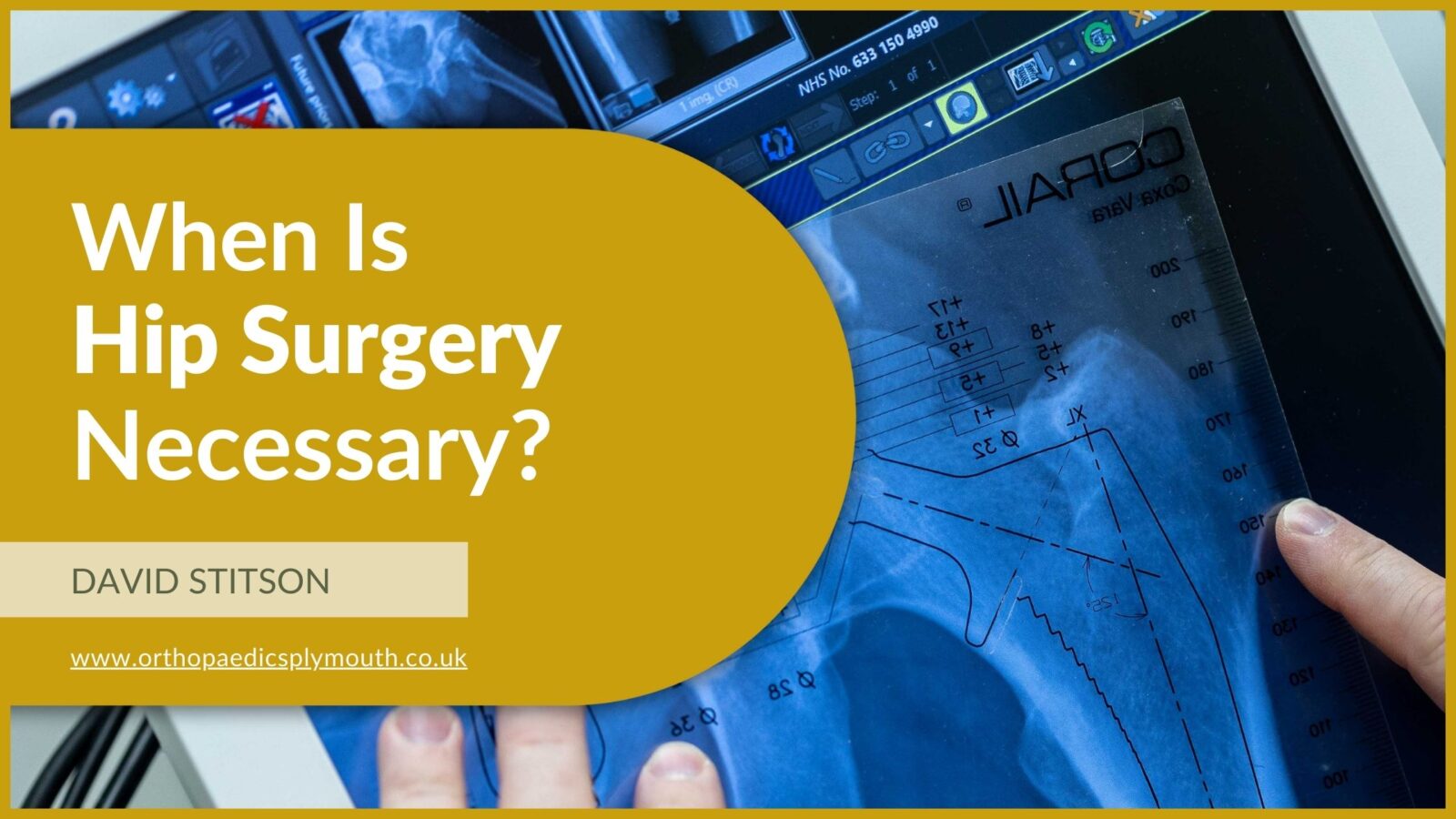
Hip pain can significantly impact your quality of life, limiting your ability to walk, exercise, or even perform basic daily activities. While many people can manage hip pain through conservative treatments like physiotherapy, medications and lifestyle changes, there are times when hip surgery becomes necessary.
Contents
ToggleUnderstanding when surgery is the best option and what types of surgeries are available can help you make informed decisions about your treatment.
When Is Hip Surgery Necessary?
Hip surgery is typically considered when other treatments fail, or no longer help, to provide adequate relief or when the underlying condition of the hip joint is severe. Here are some common scenarios where hip surgery may be recommended:
Advanced Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the hip joint to wear away, leading to pain, stiffness and reduced mobility. When the pain becomes severe and interferes with daily activities and non-surgical treatments like physiotherapy or anti-inflammatory medications are no longer effective, hip surgery may be appropriate and indicated.
Hip Fractures
A hip fracture, often caused by a fall or trauma, is a serious condition that typically requires surgical intervention. In elderly patients, particularly those with osteoporosis, hip fractures are common and can be life-threatening without prompt surgical intervention.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation in the joints. When this condition affects the hip, it can lead to significant joint damage. Hip surgery may be necessary to alleviate pain and restore function when other treatments fail.
Avascular Necrosis (Osteonecrosis)
Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to the hip bone is disrupted, leading to the death of bone tissue. This condition can cause severe pain and collapse of the hip joint. Surgery is often required to replace the damaged bone and restore joint function.
Hip Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a congenital condition where the hip socket does not fully form and so does not cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. This can lead to congenital hip dislocation in infancy or ongoing instability and premature degenerative change in later life. In severe cases, surgery may be needed in childhood to correct the condition and prevent further complications. Hip replacement as a young adult may also be required.
Labral Tears
The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the hip socket. A tear in the labrum can cause pain, clicking, or locking of the hip joint. When conservative treatments do not resolve the issue, surgery may be required to repair the labrum.
Persistent Hip Pain Unresponsive to Treatment
If hip pain persists despite months of conservative treatment and your quality of life is significantly impacted, surgery might be the best option to alleviate pain and restore mobility.
Types of Hip Surgeries
Several types of hip surgeries are available and performed by Mr Fitton, depending on the condition and the extent of damage to the hip joint. Here are the most common surgical options:
Total Hip Replacement (Arthroplasty)
In a total hip replacement, the damaged or diseased parts of the hip joint are removed and replaced with artificial components, typically made of metal, ceramic or plastic. This type of hip surgery is highly effective for patients with severe osteoarthritis, avascular necrosis, or rheumatoid arthritis. Recovery time can vary, but most patients regain significant mobility and experience a substantial reduction in pain.
Hip Resurfacing
Hip resurfacing is an alternative to total hip replacement, particularly for younger, more active patients. Instead of removing the entire hip joint, the damaged surfaces are capped with a smooth metal or ceramic covering. The surgery preserves more of the patient’s natural bone, which may make it easier to perform a future total hip replacement if needed.
Hip Fracture Repair (Fixation)
For hip fractures, Mr Stitson may use screws, plates, or rods to stabilise the broken bone. The specific approach depends on the type and severity of the fracture. In some cases, a partial hip replacement (hemiarthroplasty) may be necessary, in others a total hip replacement may be appropriate.
Hip Labral Repair
During hip labral repair, either the torn part of the labrum is removed or reattached to the hip socket. This surgery is usually performed arthroscopically, meaning that it is a type of minimally invasive hip treatment involving only small incisions. Recovery may be quicker than with more extensive surgeries, however, rehabilitation is essential to restore full hip function.
READ: Hip Replacement Rehabilitation Exercises
Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO)
PAO is a surgical procedure that can be used to treat hip dysplasia. The bone of the pelvis is cut to allow repositioning of the hip socket to better cover the femoral head. The aim of this is to help stabilise the hip joint and prevent future arthritis. This hip surgery is typically recommended for younger patients with hip dysplasia who do not yet have significant arthritis.
It is essential to discuss all your options with Mr Stitson, who can guide you through the treatment process and advise on how you can achieve the best possible outcome.
Understanding the different types of hip surgery
Understanding the different types of hip surgery and their indications can help you make an informed choice about your hip treatment. If you are experiencing persistent hip pain or have been diagnosed with a condition that may require surgery, it is essential to discuss all your options with a consultant orthopaedic surgeon, like Mr Stitson, who can guide you through the process and help you achieve the best possible outcome.
Hip surgery is a major decision that should be made with careful consideration and consultation with your healthcare provider and Mr Stitson. Hip surgery becomes necessary when non-surgical treatments cease to alleviate pain or when the hip joint is significantly damaged.
About Hip Surgery
Hip replacement surgery replaces the worn-out painful and stiff hip joint with a new prosthetic joint. This procedure is normally performed under spinal anaesthesia and is commonly followed by a night or two in the hospital. Day-case hip replacement surgery may be an appropriate option for you.

About Mr Stitson
David Stitson is a Plymouth-based Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon. Trained both in the UK and internationally, he has worked in medicine for more than 20 years for the NHS, for the Royal Air Force and in private practice. Mr Stitson operates privately at the Nuffield Health Hospital, Plymouth.

The Nuffield Plymouth CQC Rating
The Nuffield Hospital has a history that spans over half a century and has built a reputation for high standards of care, professionalism and expertise in delivering health services. They aim for continuous quality improvement in everything they do.
Active Quality and Governance programmes are in place at the Nuffield Hospital Plymouth. As part of this, the hospital is inspected by independent healthcare regulators to ensure it meets the fundamental standards of quality and safety as determined by the regulating body (CQC).
In the most recent inspection, Plymouth Nuffield Hospital was rated as ‘Good’ overall, however, the surgical element of the inspection was rated as ‘Outstanding’. The hospital was referred to as:
“Outstanding in effective and caring, and
Good in safe, responsive and well-led.”